About NASH
Learn more about NASH and Lanifibranor, NATiV3 trial’s investigational drug
About NASH
NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, is a progressive and chronic liver disease characterized by accumulation of fat in the liver. It is characterized by inflammation and damage of the liver cells that can lead to the development of scarring in the liver (e.g. fibrosis).
For some patients affected by NASH, the inflammation and damage to the liver may be reversible, but for others, it will continue to progress and worsen.
Excessive scarring on the liver may evolve to more serious stages of liver disease such as, cirrhosis (late stage scarring of the liver), and/or liver failure. It can also progress to liver cancer or may require a liver transplant.

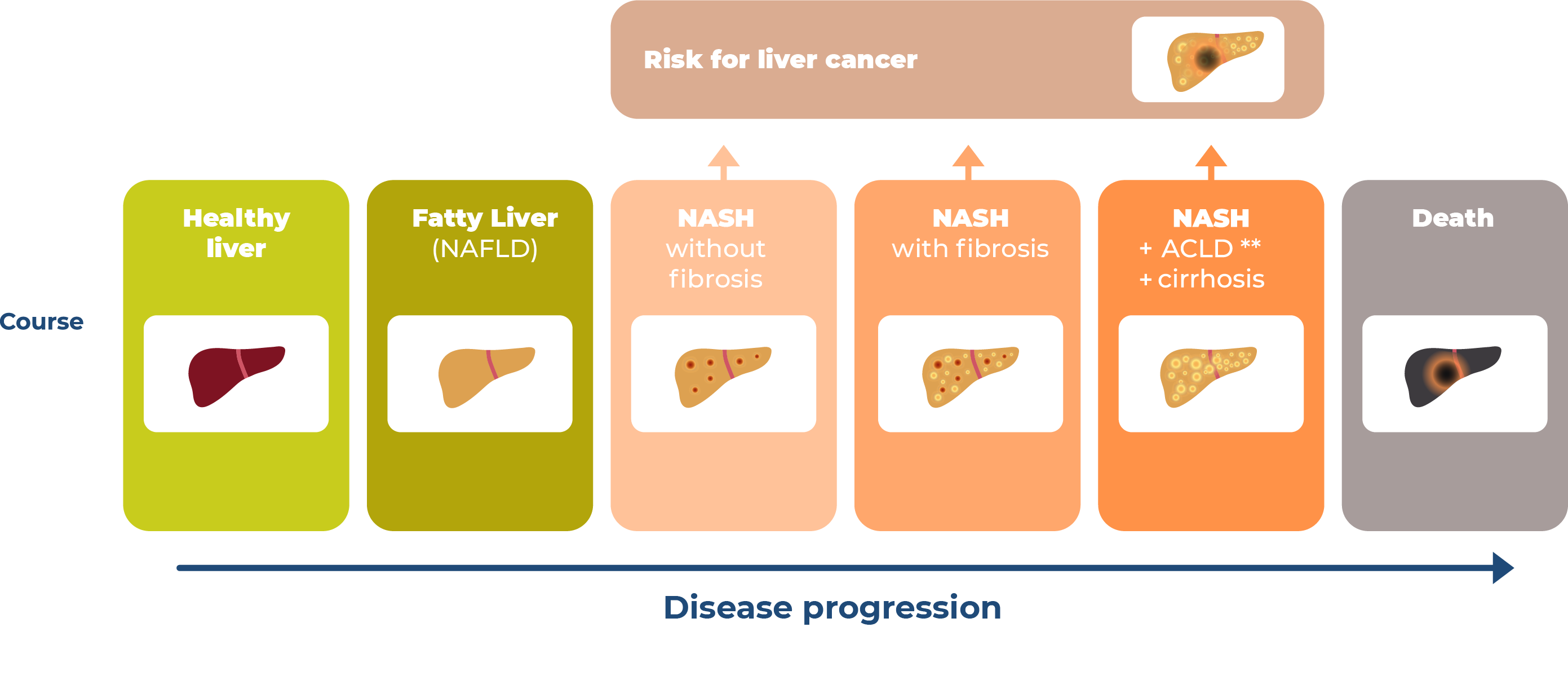
Although NASH affects a growing number of people, there is still no approved treatment for the condition. There is an urgent need to develop treatment options for patients with NASH and clinical research is essential to this process. This clinical trial is an important step in that process.
Symptoms of NASH
Patients with the earliest forms of NAFLD and NASH generally experience no symptoms or no liver specific symptoms. In some cases, patients can experience
- fatigue
- sleep apnea
- and/or pain in the upper right abdomen.
While the disease seems “silent” or without obvious symptoms, it may progress to a more serious stage and lead to a form of liver disease with more symptoms and complications.
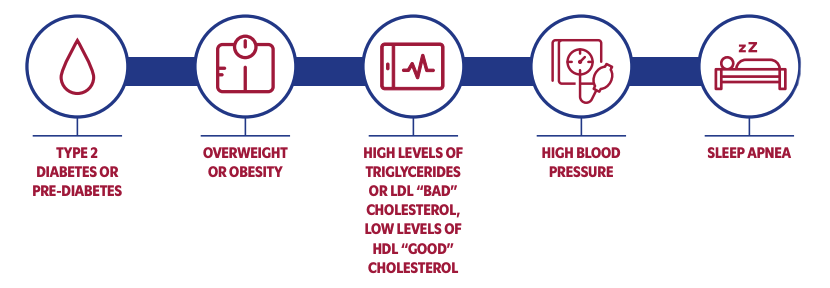
Who is at risk for NASH?
If you suffer from type 2 diabetes, obesity or are overweight, you are at a higher risk to develop NASH.
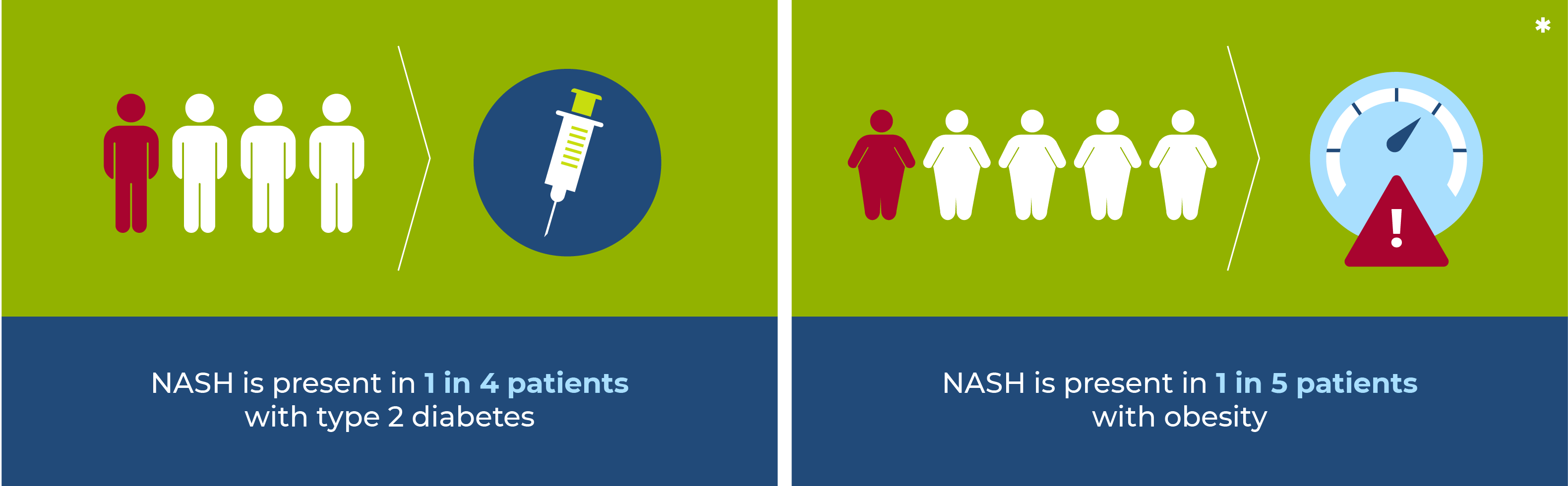
* Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2019;69(6):2672-2682. doi:10.1002/hep.30251
** ACLD: Advance Chronic Liver Disease
Current treatment
Today, there is no approved treatment for NASH. The current solutions for patients focus on lifestyle style changes, healthy diet, exercise and weight loss, which may be difficult to achieve and maintain over time.
For more information about NASH, visit the Patient Guideline published by the European Association for the Study of the Liver or visit one of the liver patient groups listed below.
Learn more
The links below provide additional information about liver function, NASH, clinical trials, and other organizations that work to promote education, treatment, and research options for liver disease.
Patient Advocacy Groups






